Formation of Image by Spherical Mirror
Formation of Image by Spherical Mirror: Overview
This topic explains concepts such as Image Formation by a Spherical Mirror, Images by Concave Mirror for Different Positions of an Object, Image Formation by Concave Mirror, Images by Convex Mirror for Different Positions of an Object, etc.
Important Questions on Formation of Image by Spherical Mirror
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror is . When an object is placed at A, its image is formed at B. If the size of image is half that of the object, then calculate the distance between A and B.
A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
Write a short note on the image formation by convex mirror.
If the length of the object is then find the length of the image. Given that the focal length of the mirror is .
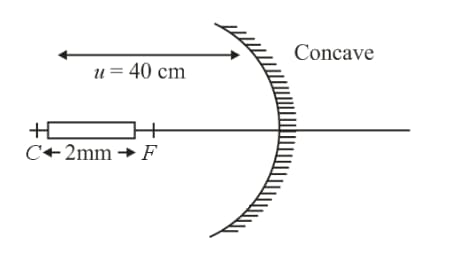
Name the mirror which can show the size of the object to be double of its original.
A student get a real image of an object of height of , when kept at from a spherical mirror of focal length . What is the type of mirror he/she used? What is the position, nature and size of the image formed?
A student get a virtual image of an object of height of , when kept at from a spherical mirror of focal length . What is the type of mirror he/she used? What is the position, nature and size of the image formed?
Image of an object situated at a distance of from a convex mirror is formed at a distance of from the mirror. Find the focal length of convex mirror.
For magnification in spherical mirrors, the object height is taken:
What will be magnification when object is at infinity in front of a concave mirror.
A high object is placed at a distance of from a convex mirror of focal length . Find the position, size and nature of the image formed by the mirror.
The distance between a real object and its image in a convex mirror of focal length is . Find the size of the image, if the object size is .
A dentist uses a spherical mirror that produces an upright image that is magnified four times. What kind of mirror is it? What is its focal length in terms of the object distance?
A concave mirror has a focal length of . A rod of length is placed along the principal axis of the mirror in such a way that the end closer to the mirror lies on its centre of curvature. The length of the image of the rod is
How the real image is inverted in the spherical mirror?
An object of height is placed in front of a concave mirror and virtual image of height is obtained. If the object is placed at from the concave mirror, the focal length of mirror is
Draw the ray diagram when of image formed the object is kept beyond of the concave mirror. With the help of the diagram mention the position and nature of the image formed. ( : Centre of curvature of mirror).
What are the properties formed by the images formed by spherical mirrors?
A concave mirror is used as a rear-view mirror in cars.
